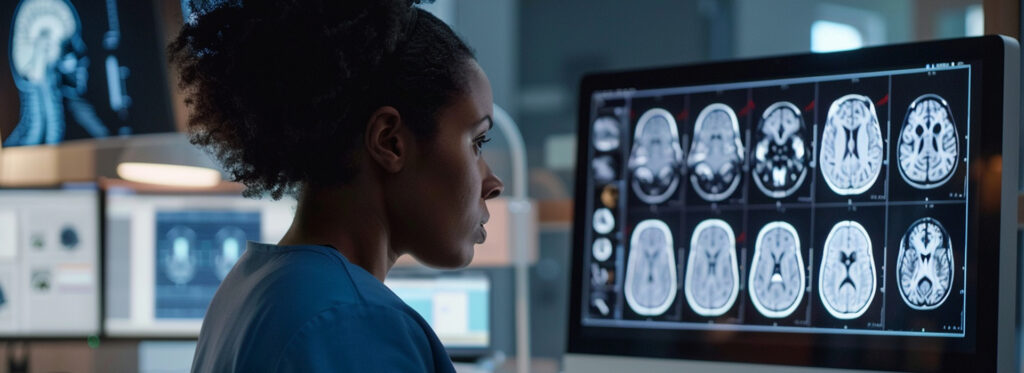
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the field of teleradiology and enhancing its precision and efficiency. AI’s integration into this domain promises improvements in diagnostic accuracy, workflow efficiency, and overall accessibility, thus enhancing the patient outcomes and revolutionizing the delivery of services in healthcare.
One of the most significant contributions of AI in teleradiology is its ability to enhance diagnostic accuracy. Traditional teleradiology depends heavily on the expertise of radiologists, who remotely interpret a vast array of images. However, chances of human error are there, particularly when radiologists are overwhelmed with high volumes of studies or when interpreting subtle abnormalities. AI algorithms, especially those based on deep learning, can analyse medical images with remarkable precision. Trained on large datasets, these AI models can detect patterns and anomalies that may escape human eyes, providing a second layer of scrutiny. Studies have shown that AI can match or even surpass human radiologists in identifying conditions like lung nodules, breast cancer, and neurological disorders. By flagging suspicious findings and highlighting areas of concern, AI helps the radiologists in making more accurate diagnoses, thus, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving the outcome of patient care.
Efficiency is another domain where AI significantly impacts teleradiology. Radiologists often face the challenge of interpreting a large number of imaging studies within shorter time frames especially in ER cases, which can delay diagnosis and treatment. AI-powered tools can streamline this process by quickly analysing images and providing preliminary reports. These tools can prioritize cases based on the severity of findings, ensuring that urgent cases receive immediate attention. For example, AI algorithms can detect critical conditions like intracranial haemorrhages or pulmonary embolisms and alert radiologists, enabling swift intervention. This capability not only speeds up the diagnostic process but also optimizes radiologists workflow, allowing them to focus on complex cases that requires their expertise.
AI’s role in image enhancement and reconstruction further strengthens its benefits in teleradiology. Images acquired from remote may often be of lower quality due to limitations in imaging equipment or transmission issues. AI algorithms can enhance these images by reducing noise, correcting artifacts, and improving resolution, ensuring that the radiologists receive clear and accurate images for interpretation. This capability is especially necessary in teleradiology, where the quality of transmitted images can directly impact the diagnostic decisions.
Another significant advantage of AI in teleradiology is its potential to provide access to high-quality radiological services. In many regions, particularly in rural areas, access to specialized radiologists is limited. AI can bridge this gap by providing diagnostic support to healthcare providers in these areas. AI algorithms can perform initial image assessments and generate diagnostic reports, which can then be reviewed by remote radiologists. This collaborative approach ensures that patients in remote locations receive timely and accurate diagnoses, thus improving access to essential healthcare services.
The integration of AI into teleradiology also holds promise for advancing personalized medicine. By analysing imaging data alongside other clinical information, such as EHR and genomic data, AI can provide comprehensive insights into a patient’s condition and can predict a patient’s response to specific treatments based on imaging features and clinical history, allowing for personalized therapeutic strategies that improve patient outcomes.
Despite its numerous advantages, the adoption of AI in teleradiology comes with challenges. Ensuring the accuracy and reliability of AI algorithms is paramount, as errors can have serious implications for patient care. Robust validation and continuous monitoring of AI tools are necessary to maintain high standards of diagnostic performance. Additionally, ethical considerations related to data privacy and algorithmic bias must be addressed. Collaborative efforts among radiologists, AI developers, and regulatory bodies are essential to overcome these challenges and establish guidelines for the safe and effective use of AI in teleradiology.